RADIUS Management¶
This section provides a centralized interface for managing AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting) configurations.
To ensure modularity and ease of maintenance, Avalon uses a Service Chaining logic. Instead of repeating IP addresses and secrets on every device, you define them once as objects and reference them hierarchically.
Chaining logic¶
A complete configuration breaks down into three services:
- User (optional): A user declared on the device that will be used to test RADIUS server functionality.
- Radius Server: The definition of a RADIUS server. Avalon can associate a user account that you have previously defined.
- Radius Group: References one or more RADIUS servers and defines certain common parameters (source interface).
RADIUS Servers¶
Definition of external authentication servers.
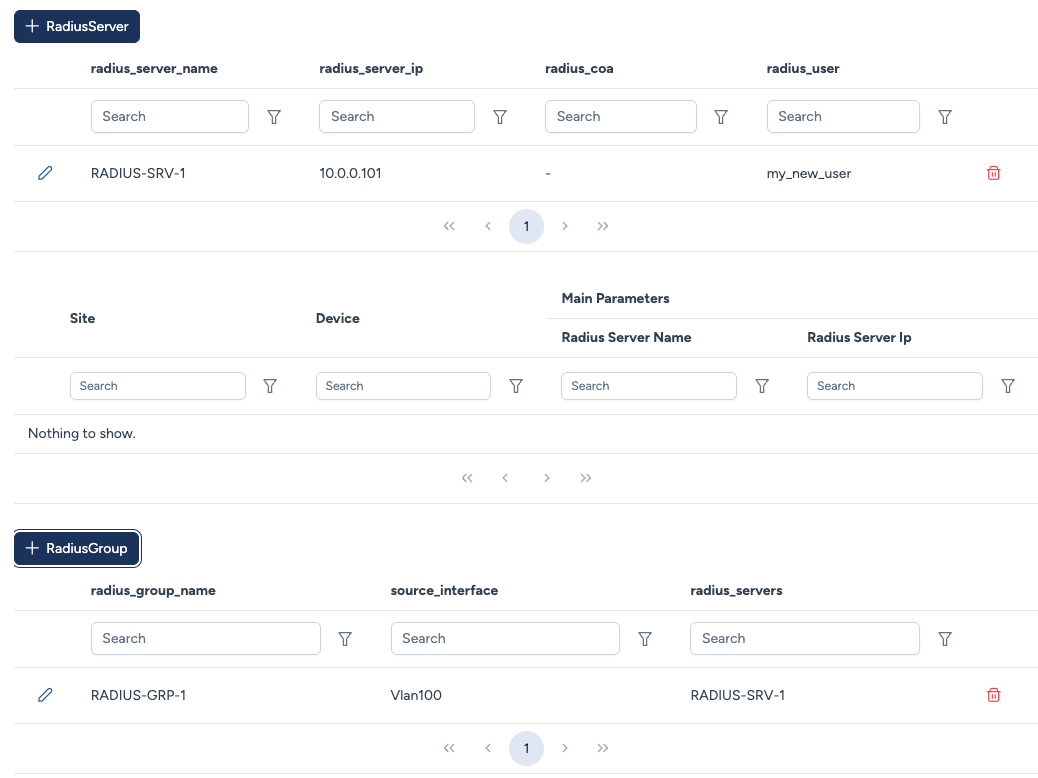
Creating a server definition¶
When adding a server, you can link it to a previously defined User object.
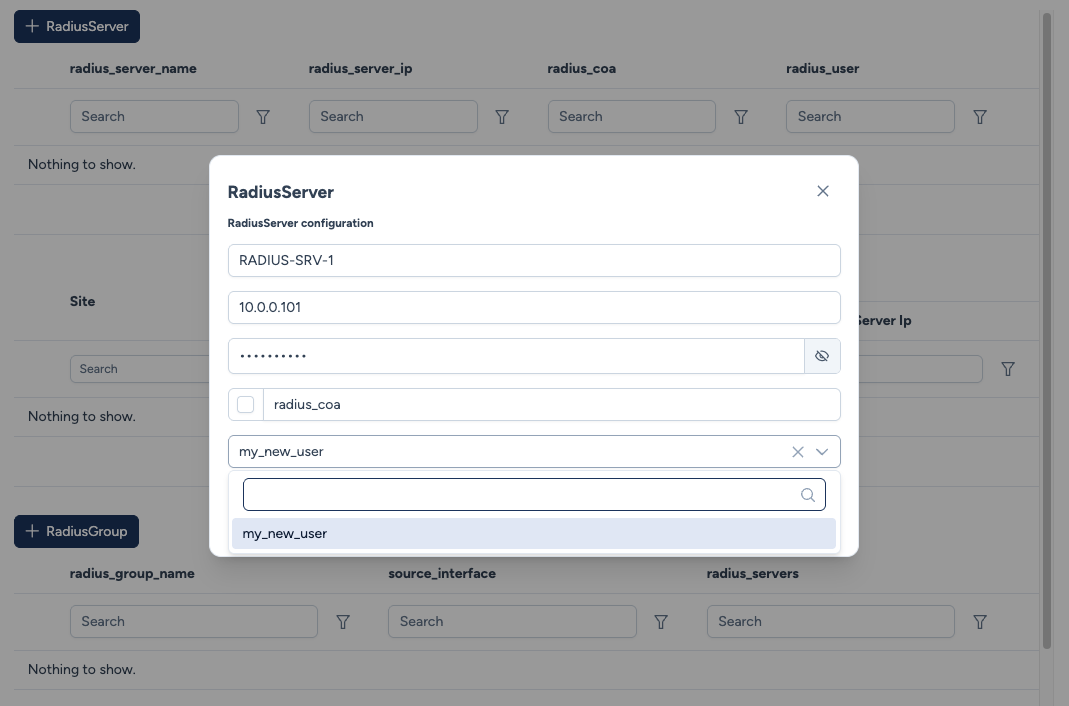
Configuration parameters:
- Radius Server Name: A logical label (e.g.,
RADIUS-SRV-1). - Server IP: The IPv4 address of the RADIUS server.
- Shared Secret: The pre-shared key for encryption.
- Radius User: Dropdown menu to select a user profile defined in Users. This allows the device to periodically verify if the RADIUS service is operational. (e.g., Cisco
automate-tester)
RADIUS Groups¶
Grouping servers into a single logical entity.
Creating a group and managing interfaces¶
When creating a group, you select member servers and the source interface:
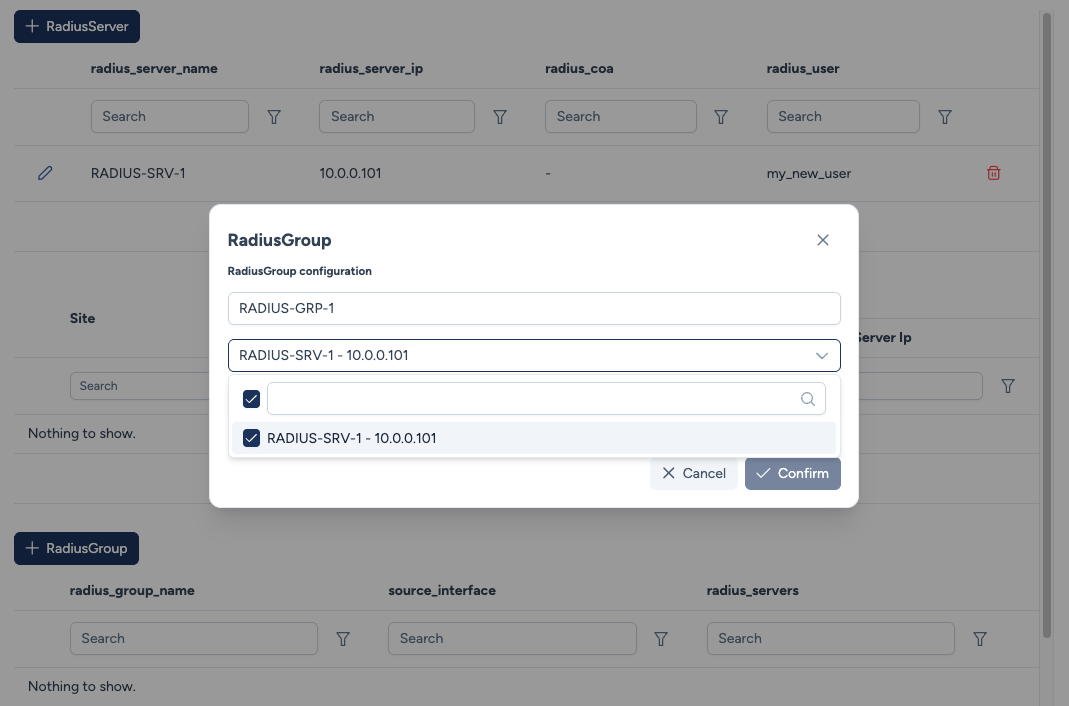
Configuration parameters:
- Radius Group Name: The unique identifier for the group (e.g.,
RADIUS-GRP-1). - Source Interface: The interface used by the device to communicate with the RADIUS server (e.g.,
Vlan100orLoopback0). - Radius Servers: A dropdown menu to choose which RADIUS Servers belong to this group.
Important: Source Interface Strategy¶
The source interface is a static text field. The entered value (e.g., Vlan100) will be deployed to all devices where this service is assigned.
- Standard usage: Homogeneous environments where all devices use the same management VLAN ID.
- Advanced usage: For dynamic source selection (distinct VLANs per site or use of different interface types: Loopbacks, physical interfaces, SVI etc.), do not use this standard module.
Advanced process: Engineering Rules
For scenarios where the source interface will vary based on device model, use Custom Services combined with Engineering Rules:
- Custom service definition: Define a service with a parameter of type Interfaces.
- Engineering Rule: Use the rules engine to automatically populate the Interfaces parameter during instantiation (e.g., 'Interfaces carrying subnets 10.1.1.0/24 or 10.1.2.0/24').
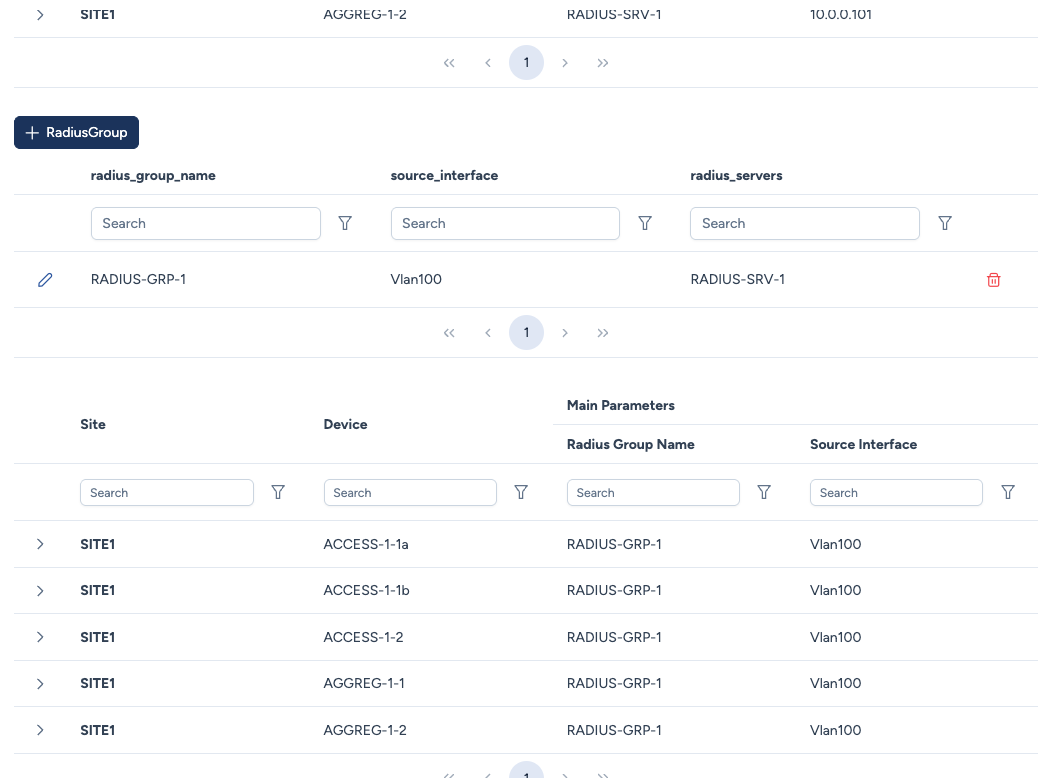
Service Instances - Deployment¶
The bottom sections of the Server and Group tables display the main parameters and the Site/Device association, allowing you to audit where these definitions are active in the network.